
1
DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE CFETP 2T2X1
Headquarters US Air Force Parts I and II
Washington, DC 20330-1030 19 January 2023
AFSC 2T2X1
AIR TRANSPORTATION SPECIALTY
CAREER FIELD EDUCATION AND TRAINING PLAN
\
ACCESSIBILITY: Publications and forms are available on the e-Publishing website at
https://www.e-publishing.af.mil for downloading or ordering.
RELEASABILITY: There are no releasability restrictions on this publication.
423 Mobility Training Squadron (EC)
Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst, NJ
345 Training Squadron
Fort Gregg-Adams, VA
Transportation Proficiency Center (TPC)
Dobbins ARB, GA

2
Part I
CAREER FIELD EDUCATION AND TRAINING PLAN
AIR TRANSPORTATION SPECIALTY
AFSC 2T2X1
Table of Contents
Preface .................................................................................................................................................. 4
Abbreviations/Terms Explained ........................................................................................................... 5
Section A - General Information
Purpose ................................................................................................................................................. 9
Uses ...................................................................................................................................................... 9
Coordination and Approval .................................................................................................................. 9
Section B - Career Progression and Information
Specialty Description.......................................................................................................................... 10
Duties and Responsibilities ................................................................................................................ 10
Skill/Career Progression. .................................................................................................................... 10
Apprentice (3) Level
Journeyman (5) Level
Craftsman (7) Level
Superintendent (9) Level
Training Decisions.............................................................................................................................. 11
Community College of the Air Force ................................................................................................. 11
Enlisted Career Field Path .................................................................................................................. 13
Section C - Skill Level Training Requirements
Purpose ............................................................................................................................................... 15
Specialty Qualification ....................................................................................................................... 15
Apprentice (3) Level Training
Journeyman (5) Level Training
Craftsman (7) Level Training
Superintendent (9) Level Training
Section D – Task Qualification Training (TQT) ................................................................................ 18
Section E - Resource Constraints ....................................................................................................... 18
OPR: 345TRS/TRR
Certified by: AFCFM, HQ AF/A4LR (CMSgt Ricky A. Govin)
Supersedes: CFETP 2T2X1, 26 August 2021
Pages: 41
3
Part II
Section A - Specialty Training Standard ........................................................................................... 19
Section B - Course Objective List ..................................................................................................... 20
Section C - Support Material ............................................................................................................ 20
Section D - Training Course Index. .................................................................................................. 20
Section E - MAJCOM Unique Requirements ................................................................................... 21
Three Attachments:
1. Qualitative Requirements (Proficiency Code Key) ........................................................................ 22
2. Specialty Training Standard (STS) ................................................................................................. 23
3. Contingency/Expeditionary Training Requirements………………………………………..….…33
MASTER
SENIOR BASIC
The falcon at the center of the badge symbolizes the Air Force. It also symbolizes American military strength,
dedication, and devotion to duty of transporters who support the generation and employment of aerospace forces
across the full spectrum of warfare. In its talons, the falcon is holding the globe with three encircling arrows,
symbolic of the extensive range of our logistics support mission and capability to sustain our forces by land, sea, or
air. The olive branch surrounding the badge symbolizes the peace aerospace forces provide through a professional
transportation community.
Basic: May be worn upon award of 3-skill level
Senior: May be worn upon award of 7-skill level
Master: May be worn when member is a Master Sergeant or above with 5 years in the specialty from award of the
7-skill level and when all 9-level tasks identified in Attachment 2 Columns 4.D. are complete.

4
AIR TRANSPORTATION SPECIALTY
AFSC 2T2X1
CAREER FIELD EDUCATION AND TRAINING PLAN
Part I
Preface
1. This Career Field Education and Training Plan (CFETP) is a comprehensive core training document that
identifies life-cycle education and training requirements; training support resources; and minimum core task
requirements for a specialty. The CFETP aims to give personnel a clear path and instill a sense of industry in
career field training.
Note: Civilians occupying associated positions use Part 2 to support duty position qualification training.
2. The CFETP consists of two parts. Supervisors plan, manage, and control training within the specialty using both
parts of the plan.
2.1. Part I provides information necessary for overall management of the specialty. Section A explains how
everyone will use the plan. Section B identifies career progression information, duties and responsibilities, training
decisions, career field path and Community College of the Air Force degree requirements. Section C provides a
general sense of each skill level with specific specialty knowledge and skills and mandatory requirements for
entry, award, and retention of each skill level. Section D Indicates resource constraints such as funds,
manpower, equipment, and facilities. Section E identifies transition training plans for the 2T2X1 career field.
2.2. Part II includes the following: Section A identifies the Specialty Training Standard (STS) and includes duties, tasks,
technical references to support training, Air Education and Training Command (AETC) conducted training,
wartime tasks, core tasks, and correspondence course requirements; Section B, the Course Objective List, is
currently reserved. Section C identifies available training materials such as Air Transportation Task Training
Guides (TTGs) which were developed to support upgrade and proficiency training. These packages are located on
the following website:
https://intelshare.intelink.gov/sites/A4T/A4TS/Training/_layouts/15/start.aspx#/Qualification%20Training%20Pa
ckages%20QTPs%20%20Task%20Trainin/Forms/AllItems.aspx Section D has a training course index supervisors
can refer to for available support training. This area lists both mandatory and optional courses; Section E identifies
MAJCOM unique training requirements supervisors can use to determine additional qualification training.
3. Using this CFETP as a guide will ensure individuals in this specialty receive effective and efficient training at
the appropriate point in their career. This plan enables us to train today's work force for tomorrow's jobs. At unit
level, supervisors and trainers will use Part II to identify, plan, and conduct training commensurate with the overall
goals of this plan.
5
ABBREVIATIONS/TERMS EXPLAINED
Advanced Training (AT). Formal course that provides individuals who are qualified in one or more positions of
their Air Force specialty with additional skills and knowledge to enhance their expertise in the career field. Training
is for selected career Airmen at the advanced level of the Air Force specialty.
Air Force Career Field Manager (AFCFM). Representative appointed by the respective HQ USAF Deputy Chief
of Staff or Under Secretariat, to ensure assigned AF specialties are trained and utilized to support AF mission
requirements. AF Career Functional Manager is the OPR; however, works in concert with MAJCOM Functional
Managers as required.
Air Force Enlisted Classification Directory (AFECD). The directories contain the official specialty descriptions
for all military classification codes and identifiers which are used to identify each Air Force job (valid requirement)
and describe the minimum mandatory qualifications for personnel to fill these jobs. These standards are used to
procure, classify, and employ personnel; to develop career programs for initial training, retraining, and skill upgrade;
and to structure unit manpower document (UMD) positions.
Air Force Installation and Mission Support Center (AFIMSC). A single intermediate-level staff performing
major command-level installation and mission support activities. Parent organization for several field operating
agencies to include the Air Force Security Forces Center, Air Force Civil Engineer Center, Air Force Installation
Contracting Agency, the services directorate of the Air Force Personnel Center and other FOAs providing
installation support capabilities.
Air Force Logistics Readiness Board (AFLRB), Logistics Readiness Chiefs Advisory Group (LogR CAG).
Meets at the direction of HQ AF/A4 to discuss significant issues, priorities and policies. Provides advice and counsel
to HQ AF/A4 concerning the enlisted logistics readiness community and resolves problems affecting the enlisted
force and the overall mission. It also provides recommendations and initiatives for future training needs, career
progression trends, and identifies information system’s needs.
Aerial Port Expediter (APEX). An AMC/A4T aircraft cargo loading program that allows APEX designated
squadrons to load and unload C-17/C-5 aircraft in the absence of a loadmaster. The APEX Program gives
squadron’s the capability to maneuver workload to mitigate aircraft scheduling issues and/or to meet launch and
recovery timelines in accordance with prescribed instructions.
Air Reserve Component (ARC). The combination of the Air National Guard and the Air Force Reserve; together
they are called the Air Reserve Component. Air Force Policy Directive 10-3, Operation Utilization of the Air
Reserve Component Forces, establishes policy to fully integrate the Air National Guard, Air Force Reserve, and
RegAF into a single Total Force.
Air Transportation Information Systems (ATIS). Systems utilized by the air transportation career field to
process passengers and cargo into the airlift system to include systems utilized to achieve in transit visibility.
Air Transportation Distance Learning (DL). Computer-based instruction in areas directly related to items found
in the 2T2X1 STS.
Career Field Education and Training Plan (CFETP). A CFETP is a comprehensive core training document that
identifies life-cycle education and training requirements; training support resources; and minimum core task
requirements for a specialty. The CFETP aims to give personnel a clear path and instill a sense of industry in career
field training.
Continuation Training. Additional training exceeding requirements with emphasis on present or future duty
assignments.
6
Core Task. Tasks the AF Career Field Manager identify as minimum qualification requirements for everyone
within an AFSC, regardless of duty position. Core tasks may be specified for a particular skill level or in general
across the AFSC. Guidance for using core tasks can be found in the applicable CFETP narrative.
Education and Training Course Announcement (ETCA). Contains specific MAJCOM procedures, fund cite
instructions, reporting instructions, and listings for those formal courses conducted or managed by the MAJCOMs
or field operating agencies (FOAs). The Education and Training Course Announcement contains courses conducted
or administered by the AF and reserve forces and serves as a reference for the AF, DoD, other military services,
government agencies, and security assistance programs.
Exportable Training. Additional training via computer assisted, paper text, interactive video, or other necessary
means to supplement training.
Field Training. Technical, operator, and other training either a training detachment or mobile training team
conducts at operational locations on specific systems and associated direct-support equipment for maintenance and
aircrew personnel.
Instructional System Development (ISD). A deliberate and orderly, but flexible process for planning, developing,
implementing, and managing instructional systems.
Initial Skills Training. An overarching term for enlisted initial skills and (non-rated line) officer initial skills
technical training. For enlisted, it refers to a formal school pipeline, comprised of one or more courses, that results
in the award of the 3-skill-level in an Air Force specialty. For officers, it refers to a formal school pipeline comprised
of one or more courses of mandatory training needed to become qualified in their Air Force specialty.
In Transit Visibility (ITV). The ability to track the identity, status, and location of DoD unit and non-unit cargo and
passengers, patients, and personal property from origin to consignee or destination during peace, contingencies, and
war.
MAJCOM Functional Manager (MFM). An individual who is the POC responsible for MAJCOM management
of an Air Force Specialty. MFM responsibilities include coordination with the AFCFM, policy development,
training, skills management and career progression at the MAJCOM level. There are four MFMs within the 2T2
AFSC each overseeing a specific population of the career field: The MFMs are located at AFIMSC, AFRC, AMC,
and ANG.
Master Task Listing (MTL). A comprehensive list (100%) of all tasks performed within a work center and
consisting of the current CFETP or AF Job Qualification Standard and locally developed AF Forms 797 (as a
minimum). Should include tasks required for deployment and/or unit type code requirements.
Master Training Plan (MTP). Employs a strategy for ensuring the completion of all work center job requirements
by using a master task listing and provides milestones for task and prioritizes deployment/unit type code, home
station training tasks, upgrade, and qualification tasks.
myLearning. Replaced ADLS as the AF Learning Management System for enterprise-wide education & training
capabilities of 800,000 users.
myTraining. A web-based application providing real-time visibility of technical qualifications, certifications, and
training status. It duplicates or replaces the functionality of the Training Business Area.
Nuclear Weapons Related Material (NWRM). Classified or unclassified assemblies and subassemblies
(containing no fissionable or fusionable materiel) identified by the Military Departments that comprise or could
comprise a standardized war reserve nuclear weapon (including equivalent training devices) as it would exist once
separated/removed from its intended delivery vehicle.
7
Occupational Analysis (OA). Collecting and analyzing factual data on the tasks and/or knowledge performed by
AF career fields. This data is used to provide personnel and training decision-makers with factual and objective job
information which enables them to justify and/or change personnel utilization policies and programs, refine and
maintain occupational structures, and establish, validate, and adjust testing and training programs. A detailed report
showing the results of an occupational survey of tasks performed within a particular AFS.
On-the-Job Training (OJT). Hands-on, “over-the-shoulder” training or evaluation conducted to certify personnel
in both upgrade (skill level award) and job qualification (position certification training).
Proficiency Training. Additional training, either in-residence, exportable advanced training courses, or on-the-job
training, provided to personnel to increase their skills and knowledge beyond the minimum required for upgrade.
Qualification Training (QT). Performance training designed to qualify an Airman who has transferred from one
base or position to another specific position. The supervisor performs an initial evaluation that includes a review of
all previously certified tasks checked against the newly assigned position’s required tasks. Any tasks not previously
completed is now required and this identifies that the member requires qualification training for the newly assigned
duty position.
Qualification Training Package (QTP). An instructional package designed for use at the unit to qualify or aid
qualification in a duty position, program, or on a piece of equipment. It may be printed, computer-based, or in other
audiovisual media.
Resource Constraints. Resource deficiencies, such as money, facilities, time, manpower, and equipment that
preclude desired training from being delivered.
Special Experience Identifier (SEI). SEIs may be used when specific experience or training is critical to the job
and no other means is appropriate or available.
Specialty Training. Training process used to qualify Airmen in their assigned specialty.
Specialty Training Requirements Team (STRT). Air Force career field managers use this forum and quality
control tool to determine and manage career field education and training requirements. For the Air Transportation
career field, the STRT includes representation from Regular Air Force, Air National Guard, and the Air Force
Reserve, to provide a Total Force perspective on career field decisions and future direction.
Specialty Training Standard (STS). An AF publication that describes an AF Specialty in terms of tasks and
knowledge an Airman in that specialty may be expected to perform or to know on the job. Also identifies the
training provided to achieve a 3-, 5-,7-, or 9-skill level within an enlisted AF Specialty. It further serves as a contract
between AETC and the functional user to show which of the overall training requirements for an AFSC are taught
in formal schools and correspondence courses.
Standard. An exact value, a physical entity, or an abstract concept, the appropriate authority, custom, or common
consent sets up and defines to serve as a reference, model, or rule in measuring quantities or qualities, developing
practices or procedures, or evaluating results. A fixed quantity or quality.
Task Qualification Training (TQT). Training conducted after Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and
High-Yield Explosive defense classroom training in which individuals perform wartime mission essential tasks in
a simulated wartime environment while wearing full ground crew individual protective equipment or aircrew
individual protective equipment. Headquarters AF, MAJCOM and local Functional Area Managers identify
wartime mission essential tasks. See AFI 10-2501, Emergency Management Program additional information/
requirements.
Task Training Guide (TTG). Standardized unit-level training and evaluation source documents used throughout
the air transportation community and will be completed prior to signing off associated tasks.
8
Total Force. Organizations, units, and individuals that comprise the Air Forces’ resources for meeting its mission.
This includes RegAF, Air National Guard, and Air Force Reserve military personnel, and civilian personnel.
Transportation Proficiency Center (TPC). Located at Dobbins ARB, GA, the Air Force Reserve Command TPC
provides 2T2X1 AFSC training to Active Duty, Guard and Reserve personnel. The TPC offers training for Air
Transportation initial, supplemental, and advanced training requirements through in-residence courses, distance
learning, and mobile training teams (MTT). The TPC also provides additional specialized transportation training
for DoD Total Force personnel and partner agencies.
Upgrade Training (UGT). Mandatory training that leads to attainment of higher level of proficiency.
Utilization and Training Workshop (U&TW). Career field managers use the utilization and training workshop
process to develop and review training programs within an Air Force specialty or civilian occupational series. The
goal of the utilization and training workshop process is to develop the architecture for effective life-cycle training
to be provided at appropriate points throughout a career path and to ensure that personnel within the specialty or
series are properly employed. For the Air Transportation career field, the U&TW includes representation from
Regular Air Force, Air National Guard, and the Air Force Reserve, to provide a Total Force perspective on career
field decisions and future direction.
9
Section A - General Information
1. Purpose. This CFETP provides information necessary for the AFCFM, MAJCOM functional managers (MFMs),
commanders, training managers, supervisors and trainers to plan, develop, manage, and conduct an effective career
field training program. This plan outlines the training that individuals in this AFS should receive in order to develop
and progress throughout their career. This plan identifies initial skills, upgrade, qualification, advanced, and
proficiency training. Initial skills training is the AFS specific training an individual receives upon entry into the Air
Force or upon retraining into this specialty for award of the 3-skill level. Normally, this training is conducted by
AETC at one of the technical training centers. Upgrade training identifies the mandatory courses, task qualification
requirements, and correspondence course completion requirements for award of the 3-, 5-, 7-, 9-skill levels.
Qualification training is actual hands-on task performance training designed to qualify an airman in a specific duty
position. This training program occurs both during and after the upgrade training process. It is designed to provide
the performance skills/knowledge required to do the job. Advanced training is formal specialty training used for
selected Airmen. The CFETP has several purposes, to include:
1.1. Serves as a management tool to plan, manage, conduct, and evaluate a career field-training program. Also, it is
used to help supervisors identify training at the appropriate point in an individual's career.
1.2. Identifies task and subject knowledge training requirements for each skill level in the specialty and recommends
education/training throughout each phase of an individual’s career.
1.3. Lists training courses available in the specialty, identifies sources of training, and the training delivery method.
1.4. Identifies major resource constraints that impact full implementation of the desired career field training process.
2. Uses. The plan will be used by MFMs and supervisors at all levels to ensure comprehensive and cohesive training
programs are available for each individual in the specialty.
2.1. AETC, 423 MTS (EC), and the TPC training personnel will develop/revise formal resident, non-resident, field
and exportable training based on requirements established by the users and documented in Part II of the CFETP.
They will also work with the AFCFM to develop acquisition strategies for obtaining resources needed to provide
the identified training.
2.2. MFMs will ensure their training programs complement the CFETP mandatory initial, upgrade, and proficiency
requirements. Identified requirements can be satisfied by OJT, resident training, contract training, or exportable
courses. MAJCOM-developed training to support this AFSC must be identified for inclusion into the plan.
2.3. Each individual will complete the mandatory training requirements specified in this plan. The lists of courses
in Part II will be used as a reference to support training. Active training records must be maintained for SMSgts
and below.
3. Coordination and Approval. The AFCFM is the approving official and waiver authority for any changes to,
and deviations from, this CFETP. The AFCFM will initiate an annual review of this document to ensure currency
and accuracy. MAJCOM representatives and AETC training personnel will identify and coordinate on the career
field training requirements. Using the list of courses in Part II will mitigate duplicate training.
10
Section B - Career Progression and Information
1. Specialty Description.
1.1. Performs and manages air transportation activities. Plans, schedules and processes eligible passengers and cargo
for air movement. Loads and unloads passengers, cargo, and baggage moved on military and commercial-contract
aircraft. Prepares and maintains air movement records and reports. Performs aircraft cleaning services and delivers
meals and comfort item supplies to aircraft. Operates forklifts and aircraft loading equipment. Uses computer
systems to provide in transit visibility over passenger and cargo movement operations. Provides installation
readiness training (cargo preparation, aircraft loading/offloading, hazardous material preparation, passenger
processing, etc.) and unilateral aircrew training. Related DoD Occupational Subgroup: 155300.
1.2. Duties and Responsibilities.
1.2.1. Supports the Department of Defense’s capability to move passengers and air cargo worldwide. Plans,
organizes, directs, coordinates, and controls air transportation activities. Determines and justifies personnel,
equipment, and facilities required to accomplish air transportation functions. Supplements policies, directs
personnel, and establishes procedures to process, load, document, and report passengers and cargo transported by
air. Inspects airlift activities for compliance and recommends corrective action. Conducts personnel and equipment
management surveys, and provides technical assistance as required. Enforces safety, quality control, and security
measures.
1.2.2.. Offers customers information on flight schedules, routes, air movement requirements, baggage limitations,
and specifics on local facilities. Performs procedures to check in, process, schedule, transport, and escort passengers
to and from aircraft. Ensures all passenger border clearance requirements have been met. Operates terminal security
equipment and conducts passenger and baggage security inspections. Reviews passenger travel authorizations for
validity and accuracy. Applies tariff rates, collects fares, and accounts for documents and monies. Uses automated
systems to provide in transit visibility and to document passenger movement operations. Develops procedures for
handling special category passengers.
1.2.3. Verifies eligibility of cargo offered for airlift. Ensures all cargo documentation, packaging, labeling and
marking requirements, and border clearance requirements have been met. Determines quantity and type of cargo to
be loaded according to aircraft allowable cabin load. Selects, assembles, palletizes, and transports cargo loads to
and from aircraft and storage areas. Checks cargo against manifests and annotates shipment overages, shortages, or
damages. Secures cargo with appropriate restraint equipment. Uses automated systems to provide in transit visibility
and to document cargo movement operations. Determines and implements necessary safety and security precautions
for handling and storing hazardous materials, special cargo, mail, and baggage.
1.2.4. Performs air terminal operations and fleet service functions. Prepares, completes, and maintains air movement
records, documents, and reports. Selects loads, prepares load plans, and computes aircraft center of balance. Plans
and manages fleet service activities to provide cleaning, lavatory servicing, and meal delivery on aircraft. Completes
actions to requisition, store, and issue expendable and nonexpendable items for use on aircraft.
2. Skill/Career Progression. Adequate training and timely progression from the apprentice to the superintendent
skill-level play an important role in the Air Force's ability to accomplish its mission. Active training records must
be maintained for SMSgts and below. It is essential that everyone involved in training do their part to plan, manage,
and conduct an effective training program. The guidance provided in this part of the CFETP will ensure each
individual receives viable training at appropriate points in their career.
2.1. Apprentice, 3-Level. Upon completion of initial skills training by attending the Air Transportation Apprentice
Course, trainees will work with a trainer to enhance their knowledge and skills. They will utilize the MTL for the
assigned duty position, and other exportable courses to progress in the career field. Once qualified on a task ("signed
off"), a trainee may perform the task unsupervised. Note: With 2T2 CFM approval, ARC MFMs will determine
training requirements for award of 2T231 AFSC to prior service personnel. AFRC personnel with prior service

11
may complete TPC Air Transportation Basic Course.
NOTE: RegAF prior service personnel not authorized by AFPC to attend the Air Transportation Apprentice Course
may coordinate with the TPC Superintendent to send members to the TPC Air Transportation Basic Course. Based
on availability and approval, the course will be unit funded.
2.2. Journeyman 5-Level. Once upgraded to the 5-level, a journeyman will enter into continuation training to
broaden their experience base. 5-levels may be assigned job positions such as information control, passenger service
duties, fleet service duties, cargo and load team member, and various staff positions. For promotion testing purposes,
individuals will use material as designated in the Enlisted Promotions References and Requirements Catalog
(EPRRC). Members are strongly encouraged to continue their education toward a CCAF degree.
2.3. Craftsman 7-Level. A craftsman can expect to fill various supervisory and management positions such as shift
supervisor, section chief, and senior controller. They will also be assigned to work in staff positions. 7-levels should
take courses or obtain added knowledge on management of resources and personnel. For award of the 7- level, all
7-level tasks must be signed off. Members are strongly encouraged to complete academic education through CCAF
and higher degree programs.
2.4. Superintendent 9-Level. A 9-level can be expected to fill positions such as flight chief, NCOIC,
superintendent, and various staff jobs. Experience and general knowledge of air transportation systems and
mobility operations to include hub and spoke dynamics, air transportation organizational constructs, and
passenger and cargo movement procedures through the defense transportation system. Additional training in the
areas of budget, manpower, resources and personnel management should be pursued through continued education.
Additional higher education and completion of courses outside of the career AFSC are also recommended.
Note: ARC personnel must have a minimum of two years as a 2T271, proficient in all 7-level tasks, and capable
of performing shift supervision roles conducive to assigned rank before award of the 9-skill level.
3. Training Decisions. The CFETP uses a building block approach (simple to complex) to encompass the entire
spectrum of training requirements for the Air Transportation career field. The spectrum includes a strategy for when,
where, and how to meet the training requirements. The strategy must be apparent and affordable to reduce
duplication of training and eliminate a disjointed approach to training.
4. Community College of the Air Force. Enrollment in CCAF occurs upon completion of basic military training.
CCAF provides the opportunity to obtain an Associate in Applied Sciences Degree. In addition to the associate
degree program, CCAF offers the following:
4.1. Professional Certification. CCAF offers multiple professional certifications based on specific education,
experience and qualification requirements. Two certifications are listed below. For additional information on these
and other certifications, visit the CCAF web site: https://www.my.af.mil/gcss-af/USAF/content/CERT
4.2. CCAF Instructor Certification (CIC). The CIC program replaced the Occupational Instructor Certification
(OIC) on 1 January 2011. The purpose of the CIC is to recognize the instructor's extensive faculty development
training, education and qualification required to teach a CCAF course and formally acknowledges the instructor's
practical teaching experience. For more information on this certification, visit:
https://www.my.af.mil/gcss-
af/USAF/AFP40/d/s6925EC13447C0FB5E044080020E329A9/Publications/Certifications/CIC_Brochure.pdf
4.3. Air Force Credentialing Opportunities On-Line (AF COOL). Air Force COOL is a pathway for enlisted
Airmen to earn industry recognized professional certifications, licenses to enhance their active-duty work, and to
prepare them as they transition to the civilian job market. To view certification opportunities, visit AF COOL at:
https://afvec.us.af.mil/afvec/af-cool/welcome
4.4. Trade Skill Certification. When a Community College of the Air Force student separates or retires, a
trade skill certification is awarded for the primary occupational specialty. The College uses a competency-
12
based assessment process for trade skill certification at one of four proficiency levels: Apprentice,
Journeyman, Craftsman (Supervisor), or Master Craftsman (Manager). All are transcribed on the Community
College of the Air Force transcript.
4.5. Degree Requirements. All Airmen are automatically entered into the CCAF program. Prior to being awarded
an associate degree, the 5-level must be awarded, and the following requirements must be met:
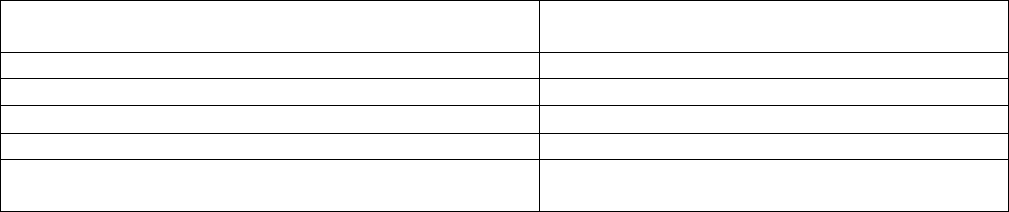
Degree Requirements
Semester Hours
Technical Education
24
Leadership, Management, and Military Studies
6
General Education
15
Program Elective
15
Total
60
4.5.1. Technical Education (24 Semester Hours): 9 semester hours must be applied from technical core courses.
The remaining semester hours are applied from either technical core or technical elective courses.
4.5.2. Leadership, Management, and Military Studies (6 Semester Hours): May be satisfied from Professional
Military Education, civilian management courses, and/or testing credit.
4.5.3. General Education (15 Semester Hours): This requirement is satisfied by application of courses accepted in
transfer or by testing credit. The criteria for application of courses to the general education requirement are provided
in the CCAF Catalog.
4.5.4. Program Elective (15 Semester Hours): Satisfied with applicable technical education; leadership,
management, and military studies; or general education requirements. This must include 6 semester hours of CCAF
degree-applicable technical course credit, otherwise not applicable to this program of enrollment. See the CCAF
Catalog for details regarding the Associates of Applied Science for this specialty.
4.5.5. Off-Duty Education. Additional off-duty education is a personal choice that is strongly encouraged.
Individuals desiring to become an Air Education and Training Command Instructor should be actively pursuing an
associate or higher degree. A degreed faculty is necessary to maintain accreditation through the Southern
Association of Colleges and Schools.
13
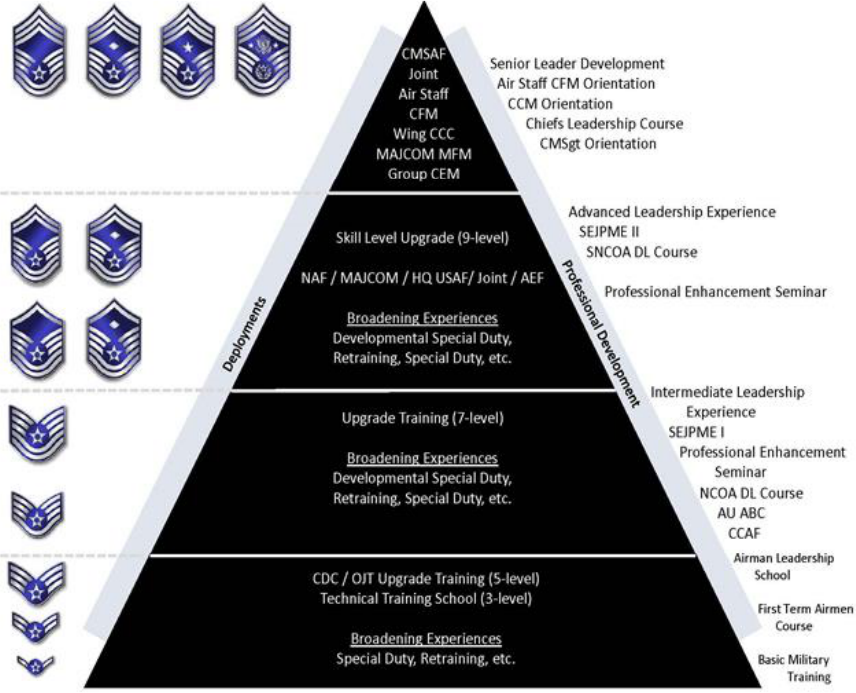
5. Enlisted Career Path. Refer to AFI 36-2670, Total Force Development to view the Enlisted Career Path. The
Enlisted Career Path provides education and training requirements, AF average promotion sew on times, high year
tenures, etc.
Functional, Career Broadening, Developmental Special Duty and Leadership Paths (Enlisted)
14
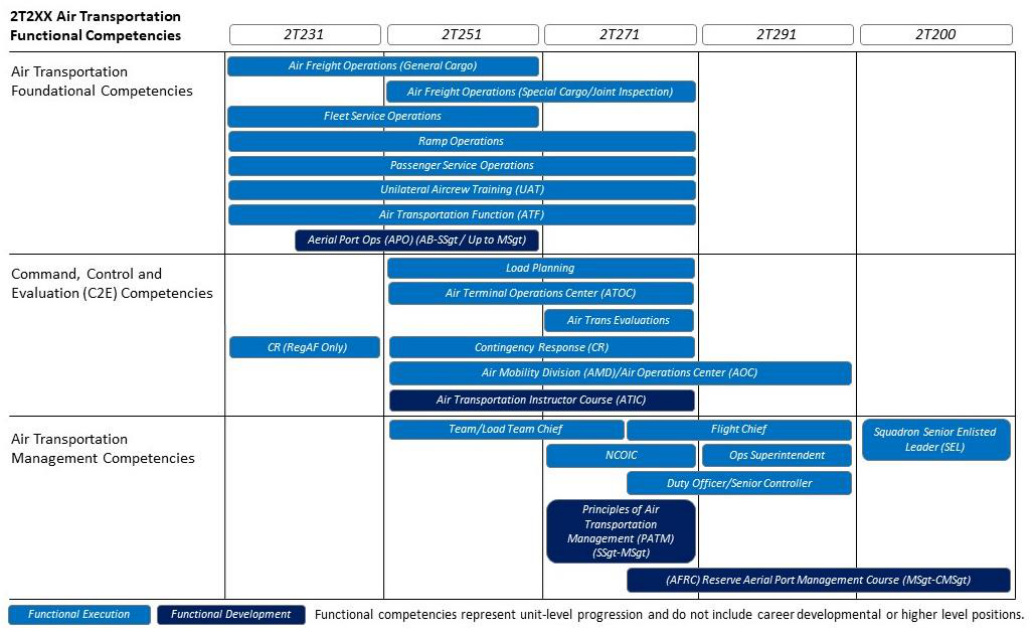
6. Career Development Path. The 2T2X1 Career Development Path depicts the timeline an Airman needs to
demonstrate competency to perform duties within the Air Transportation career field, while illustrating recommended
AFSC-specific training for personal development. The graph serves as a “roadmap” to provide consistency in how
we rotate our Airman. For example, an Airman should be competent in “Foundational Competencies” before
progressing to Command, Control and Evaluation (C2E) Competencies (i.e. proficient in passenger and cargo ops
before working ATOC). Following this roadmap ensures consistency, more proficient Airman serving in C2E and
management sections, and coincides with our deployment requirements. Leadership must make every effort to rotate
Airman throughout the available foundational competencies before moving them to C2E competencies and eventually
management positions.
2T2X1 Career Development Path
15
Section C - Skill Level Training Requirements
1. Purpose. Skill level training requirements in this career field are defined in terms of tasks and knowledge
requirements. This section outlines the specialty qualification requirements for each skill level in broad, general
terms and establishes the mandatory requirements for entry, award and retention of each skill level. The specific
task and knowledge training requirements are identified in the STS in Part II, Sections A and B of this CFETP.
2. Specialty Qualification:
2.1. Apprentice 3-Level Training:
2.1.1. Specialty Qualification.
2.1.1.1. Knowledge. Passengers and cargo movement functions to include transport aircraft types, capabilities, and
configurations; weight and balance factors; airlift transportation directives and documentation; cargo securing
techniques; border clearance requirements; operation of material handling and other types of loading equipment or
devices, fleet service functions; automated data processing equipment and its application in airlift activities;
passenger service functions, and customer relations principles; and unilateral aircrew training (UAT) methods and
equipment.
2.1.1.2 Education. For entry into this specialty, completion of high school or a general educational development
equivalency with courses in English, Computer Operation, and Mathematics is desirable.
2.1.1.3. Training. For award of 2T231 AFSC, completion of the basic air transportation course is mandatory.
Note: AFRC personnel with prior service may complete TPC Air Transportation Basic Course. In addition, these
personnel must complete knowledge training on all tasks taught in the initial skills course combined with additional
mandatory requirements identified by the AFRC MFM and approved by the 2T2 CFM. Only after completing
mandated OJT are prior service personnel awarded a 3-skill level.
2.1.1.4. Experience. After arrival at first duty station, (1) orient the trainee and conduct initial evaluations, (2)
evaluate and provide performance-based training on the tasks taught in technical school, and (3) identify and start
training in additional tasks required to fully utilize trainee in their duty position.
2.1.2. Training Sources. The 2T2X1 AFSC STS provides the knowledge and task requirements for upgrade to the
3-skill level.
2.1.3. Implementation. Entry into training occurs upon completion of basic training. 2T231 AFSC is awarded
following successful completion of the Air Transportation Apprentice Course or meeting prior service requirements
in paragraph 2.1.1.3.
2.2. Journeyman 5-Level Training:
2.2.1. Specialty Qualification.
2.2.1.1. Knowledge. Passengers and cargo movement functions to include transport aircraft types, capabilities, and
configurations; weight and balance factors; airlift transportation directives and documentation; cargo securing
techniques; border clearance requirements; operation of material handling and other types of loading equipment or
devices, fleet service functions; automated data processing equipment and its application in airlift activities;
passenger service functions, and customer relations principles; and UAT techniques and equipment This is not all
inclusive, refer to the CFETP part II for mandatory core tasks.
2.2.1.2. Training. Upgrade training to the 5-skill level in this specialty consists of the completion of all 3- and 5-
level core tasks identified in the STS. Once tasks are completed members are eligible for skill level upgrade.
There is no minimum time in training requirement. The maximum time in training requirement is 24 months for
active-duty personnel and 36 months for reserve and guard personnel.
16
2.2.1.3. Experience. Qualification in and possession of 2T231 AFSC. In addition, experience in functions such as
loading and unloading aircraft; operating automated or manual materials handling and other loading equipment and
processing, scheduling, and maintaining records related to passenger and cargo movement.
2.2.2. Training Sources and Resources. The STS identifies mandatory core task items required for upgrade.
2.2.3. Implementation. Enter personnel into 5-skill level upgrade training as of the date arrived station (DAS).
Successful completion of all 3- and 5- level core tasks identified in the STS is required for upgrade to the 5-skill
level.
2.3. Craftsman 7-Level Training:
2.3.1. Specialty Qualification.
2.3.1.1. Knowledge. Passengers and cargo movement functions to include transport aircraft types, capabilities, and
configurations; weight and balance factors; airlift transportation directives and documentation; cargo securing
techniques; border clearance requirements; operation of material handling and other types of loading equipment or
devices, fleet service functions; automated data processing equipment and its application in airlift activities;
passenger service functions, and customer relations principles; and UAT techniques and equipment. This is not all
inclusive, refer to the CFETP part II for mandatory core tasks
2.3.1.2. Training. Upgrade training to the 7-skill level in this specialty consists of the completion of all 3-, 5-, and
7-level core task items identified in the STS. Once tasks are completed members are eligible for skill level upgrade.
There is no minimum time in training requirement. The maximum time in training requirement is 24 months for
active-duty personnel and 36 months for reserve and guard personnel.
2.3.1.3. Experience. Qualification in and possession of 2T251 AFSC. In addition, experience supervising functions
such as preparing aircraft load plans; loading and unloading aircraft; operating automated and manual materials
handling equipment, processing, scheduling, and maintaining records on passenger movement by airlift.
2.3.2. Training Sources and Resources. Successful completion of 7-level core task items satisfies the knowledge
and task requirements specific for the 7-level.
2.3.3. Implementation. Personnel selected for promotion to SSgt enter 7-level upgrade training the first day of the
promotion cycle (1 September each year). STEP promotes, retrainees, and ARC personnel are entered into 7-level
upgrade training upon promotion to SSgt or completion of 5-level if already a SSgt. 7-level is awarded upon
completion of all 5 and 7-level core tasks and all duty position tasks. Attendance in the Principles of Air
Transportation Management (PATM) course is highly encouraged upon award of the 7-skill level.
2.4. Superintendent 9-Level Training:
2.4.1. Specialty Qualification.
2.4.1.1 Knowledge. Mandatory knowledge includes: passengers and cargo movement functions to include
transport aircraft types, capabilities, and configurations; weight and balance factors; airlift transportation directives
and documentation; cargo securing techniques; border clearance requirements; operation of material handling and
other types of loading equipment or devices, fleet service functions; automated data processing equipment and its
application in airlift activities; passenger service functions, and customer relations principles; and UAT techniques
and equipment.
2.4.1.2 Training. An individual must be a SMSgt, be trained/qualified to the task/subject knowledge level in
Column 4.D. of Attachment 2 and have completed all 3-, 5-,7-, and 9-level core tasks for award the 2T291 skill-
level.
2.4.1.3. Experience. Qualification in and possession of 2T271 AFSC. Also, experience and general knowledge of
air transportation systems and mobility operations to include hub and spoke dynamics, air transportation
organizational constructs and passenger and cargo movement procedures through the defense transportation system.
17
2.4.1.3.1. ARC Only. ARC personnel must have a minimum of two years as a 2T271, proficient in all seven-level
tasks, as outlined in CFETP 2T2X1, and capable of performing shift supervision roles conducive to assigned rank
before award of the 9-skill level.
2.5. Training Sources/Resources. Completion of all applicable QTPs and/or TTGs should satisfy knowledge and
experience requirements listed above. In addition, the Logistics Readiness SNCO Course will provide increased
knowledge on the entire Logistics Readiness enterprise so that Air Transportation SNCOs are better prepared to
serve in LRS leadership, staff and/or key leadership positions.
2.6. Other. The following are mandatory as indicated:
2.6.1. See Enlisted Classification Directory (ECD) for current entry requirements.
2.6.1.2. For entry, award, and retention of AFSCs 2T211/31/51, must possess a valid state driver’s license to operate
government motor vehicles (GMV) in accordance with AFI 24-301, Ground Transportation, as well as the ability to
speak distinctly and communicate well with others.
2.6.1.3. Specialty requires routine access to Secret material or similar environment. For award and retention of
2T2X1, completion of a current National Agency Check, Local Agency Checks and Credit (NACLC) according to
AFI 31-501, Personnel Security Program Management, and maintain local network access IAW AFI 17-130,
Cybersecurity Program Management, and AFMAN17-1301, Computer Security. Note: Award of the 3-skill level
without a completed NACLC is authorized provided an interim Secret security clearance has been granted according
to AFI 31-501.
2.6.1.4. Retraining into the 2T2XX career field within the Air Force Reserve or Air National Guard is restricted to
the grades of E-6 and below with less than 12 years of Total Federal Military Service.
18
Section D – Task Qualification Training (TQT)
1. Task Qualification Training (TQT). Training and certification of TQT will be accomplished IAW
DAFI 10-401, Air Force Operations Planning and Execution, DAFI 10-2501, Air Force Emergency
Management (EM) Program, DAFI 36-2670, Total Force Development, and AEF Online Tier 2A,
Expeditionary Skills (ES) Proficiency Training/Tier 2B, Home Station Pre-Deployment Training.
1.1. Task standardization is key to TQT, ensuring readiness while in a Chemical, Biological, Radiological,
and Nuclear (CBRN) Environment. All Air Transportation personnel will know the exact UTC they are
postured against. Knowing this information, supervisors/trainers will utilize Attachment 3 of this CFETP
to ensure trainees are proficient in the tasks corresponding to their assigned UTC and skill level as a
minimum. In addition, members must also be trained and qualified to perform each associated task in a
contested environment, by demonstrating proficiency in MOPP 4.
1.2. Prerequisites. CBRN Defense Awareness Course (WBT) and initial CBRN Defense Survival Course
(Hands-on).
1.3. TQT Training Frequency. Due to limited equipment/training capabilities, CBRN TQT will be
conducted IAW applicable host wing guidance and documented in accordance with unit directives, i.e.
G081, myTraining, Patriot Excalibur (PEX), or equivalent approved system. When possible, TQT will be
conducted in conjunction with wing/base exercises. CBRN TQT must include career field specific duties
performed within air terminal work centers and during vehicle operations. Individuals must be current in
CBRN Defense Awareness/Survival at the time of departure to TDY/Deployment locations and will be
considered current for the duration of the assignment.
1.3.1. Exercises. Force Modernization Trainers (FMTs) will ensure training is provided for individuals
participating in exercises where operating in CBRN environment will be expected and not falling under
the criteria outlined above.
1.4. Full Credit Requirements. Individuals successfully complete the demonstrated-performance objective.
Section E - Resource Constraints
1. Purpose. This section identifies known resource constraints which preclude optimal/desired training
from being developed or conducted, including information such as cost and manpower. Narrative
explanations of each resource constraint and an impact statement describing what effect each constraint has
on training are included. Also included in this section are actions required, office of primary responsibility,
and target completion dates. Resource constraints will be, as a minimum, reviewed and updated annually.
1.1. Three-Level Training:
1.1.1. Constraints. None.
1.2. Five-Level Training:
1.2.1. Constraints. In many cases, ARC personnel are not co-located with active flight line operations or
active-duty Aerial Port Squadrons, limiting access and ability for hands-on training. ARC personnel are
heavily reliant on the availability of Annual Tour and Seasonal Training programs to achieve the
necessary knowledge and skillsets required for 5-level upgrade. Additionally, access to CCMD and other
MAJCOM funded exercises provides ideal training environments for members gaining and exercising
new core task capabilities.
1.3. Seven-Level Training:
1.3.1. Constraints. None
19
Part II
Section A - Specialty Training Standard (STS)
1. Implementation. This Specialty Training Standard is used for technical training provided by AETC for
classes beginning (7 April 2021) and graduating (5 May 2021).
2. Purpose. As prescribed in AFI 36-2670 and this STS:
2.1. Column 1 lists the most common tasks, knowledge, and technical references (TR) necessary for airman
to perform duties in the 3-, 5-, 7-, and 9-skill level of the Air Transportation ladder of the Transportation
Career Field. During times when asked to accelerate to wartime surge, apprentice course will be taught 10
hours a day, 6 days a week.
2.2. Column 2 identifies Core Tasks and specialty-wide training. The “*” is placed in the column
corresponding to the 3-, 5-, 7-, 9- skill level to identify specialty-wide training requirements for that level.
These tasks and knowledge items are based on an analysis of the duties and responsibilities contained in the
Air Force Enlisted Classification Directory (AFECD), The Official Guide to the Air Force Enlisted
Classification Codes. Core Task STS line items are mandatory and must be completed before the 5-, 7-, or
9- skill level can be awarded.
2.3. Column 3 provides certification for on-the-job training and is used to record completion of tasks and
knowledge training requirements. If available, supervisors and trainers should use the automated training
management systems to document technician qualifications. Task certification must show a start and
completion date and include both trainer and trainee initials. Note: There are currently no tasks in the Air
Transportation career field requiring third party certification.
2.4. Column 4 identifies the proficiency to be demonstrated on the job by the formal AETC school graduate
as a result of training on the task/knowledge and the career knowledge provided by the correspondence
course.
2.5. Attachment 1 shows the qualitative requirements and the proficiency code key used to indicate the
level of training and knowledge provided by resident training, task training guides (TTGs) and career
development course (when applicable).
2.6. The STS becomes a job qualification standard (JQS) for on-the-job training when automated or
placed in AF Form 623, Individual Training Record. Document and certify completion of training IAW
AFI 36-2670, Total Force Development. Active training records must be maintained for SMSgts and
below. Tasks are trained and qualified to the “go/no go” level. “Go” means the individual can perform
the task without assistance and meet local demands for accuracy, timeliness, and correct use of
procedures.
2.7. The STS Is a guide for development of promotion tests used in the Weighted Airman Promotion
System. Specialty Knowledge Tests are developed at the AETC Airman Advancement Division, by Senior
Noncommissioned Officers with extensive practical experience in their career fields. Specialty Knowledge
Tests are developed by subject matter experts who authenticate Weighted Airman Promotion System
material and reference AF Specialty-specific occupational analysis data. Questions are based upon study
references listed in the Enlisted Promotions References and Requirements Catalog. Individual
responsibilities are in Chapter 4, paragraph 4.2.11 of AFMAN 36-2664, Personnel Assessment Program.
Weighted Airman Promotion System is not applicable to the ARC.
2.8. 2T2 AFCFM Policy Exception: Core tasks not applicable/available at home station are not required
for upgrade (units are not required to send personnel temporary duty (TDY) for core task training).
Note: ARC personnel have established mechanisms for sending personnel TDY for required upgrade
20
training, due to limited resources for hands-on training at many home station locations. All available
options for Annual Tour, Seasoning Training, formal training, and exercise participation must be
pursued for a minimum of 15 months before determining that a core task cannot be accomplished.
3. Additional Requirements: MAJCOMs will use QTPs or TTGs to train to their utmost capability based
on available equipment or tasks performed at a specific location. Partial use of QTP or TTG training steps is
authorized if not all required resources exist locally. It is not necessary to send people to off-station training
to meet requirements created by QTP or TTG compliance.
Note: ARC personnel have established mechanisms for sending personnel TDY for required upgrade
training, due to limited resources for hands-on training at many home station locations. All available
options for Annual Tour, Seasoning Training, formal training, and exercise participation must be
pursued for a minimum of 15 months before determining that training tasks outlined in a QTP and/or
TTGs cannot be accomplished
4. Recommendations:
4.1. Unit Training. Managers, superintendents, and supervisors will ensure personnel are trained on all
applicable STS items. Active-duty training records must be maintained for SMSgts and below.
4.2. Graduate Performance. Report unsatisfactory performance of course graduates and any inadequacies
of this CFETP to the 345 TRS/TRR, 711 B Avenue, Ft Gregg-Adams, VA 23801-1798, or call Customer
Service Information Line DSN 473-2917, reference specific STS paragraphs.
Section B - Course Objective List: This area is currently reserved.
Section C - Support Material: This area is currently reserved.
Section D - Training Course Index
5. Purpose. This section of the CFETP identifies training courses available for the specialty and how the
courses are used by each MAJCOM in their career field training programs.
6. Air Force In-Residence Courses.
COURSE NUMBER
TITLE
LOCATION
USER
L8ABP2T231
Air Transportation Apprentice
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
DoD
L8AZP2T051
Hazardous Material Preparer (Initial)
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
DoD
L6AZW2T051
Hazardous Material Preparer (Initial)
Mobile/Virtual
DoD
LCAZP2T251
Hazardous Material Inspector (Initial)
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
DoD
L6AZW2T251
Hazardous Material Inspector (Initial)
Mobile
DoD
L9AZA2T251
Parachute Rigger Course (PRC) Phase 1
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
DoD
AMC PATM
Principles of Air Transportation Mgmt
JB-MDL, NJ
DoD
AMC APO
Aerial Port Operations
JB-MDL, NJ
DoD
AMC ATIC
Air Transportation Instructor Course
JB-MDL, NJ
DoD
C-17 APEX
C-17 APEX Load Director
Location Determined
by 423 MTS (EC)
AMC
C-5 APEX
C-5 APEX Load Director
Location Determined
by 423 MTS (EC)
AMC
ATSEP FTC
ATSEP Formal Training Course
JB-MDL, NJ
AMC
4J3ABR2T2X1-001
Air Transportation Basic Course
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
21
4J5AAO2T251-003
Hazardous Material Inspector (Initial)
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
4J6AAO2T251-003
Hazardous Material Inspector (Initial)
Mobile/Virtual
ARC
4J3AAR2T2X1-002
ICODES Familiarization Course
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
TPC JIC
Joint Inspection Course
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
TPC JIC
Joint Inspection Course
Mobile
ARC
TPC TUN
60K Tunner Operator Course
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
TPC HAL
25K Halvorsen Operator Course
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
TPC ALPI
Air Load Planning Course (Initial)
Dobbins ARB, GA
ARC
TPC ALPI
Air Load Planning Course (Initial)
Mobile
ARC
7. Exportable Courses
COURSE NUMBER
TITLE
LOCATION
USER
L6ARW2T251
Hazardous Material Inspector
(Refresher)
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
/ MyLearning
AF
L6ARW2T051
Hazardous Material Preparer
(Refresher)
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
/ MyLearning
AF
L6AAW2XXXX
Log-R SNCO course
JBSA, TX /
MyLearning
AF Log
AFSCs
8. Courses Under Development/Revision
COURSE NUMBER
TITLE
LOCATION
USER
LCABP2T231
Air Transportation Apprentice
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
DoD
Section E - MAJCOM Unique Requirements
1. Qualification Training Package (QTP)/Task Training Guide (TTG): QTPs/TTGs are standardized
AF/unit-level training and evaluation source documents used throughout the air transportation community
and will be completed prior to signing off associated tasks in myTraining. Air transportation personnel
are directed to utilize AF-approved QTPs for vehicle/MHE training and AFSC-approved TTGs for duty
position qualification and upgrade training. Air transportation personnel will use QTPs and TTGs to train
to the utmost capability based on available equipment or tasks performed at respective locations. Partial
use of TTGs is authorized if not all required resources exist locally. It is not necessary to send people to
off-station training to meet requirements created by TTG compliance. QTPs for vehicles are located on
AF e-Publishing website and TTGs are located on the AMC/A4T SharePoint® website. The 2T2 AFCM
will manage TTG development to support air transportation CFETP line items.
Note: ARC personnel have established mechanisms for sending personnel TDY for required upgrade
training, due to limited resources for hands-on training at many home station locations. All available
options for Annual Tour, Seasoning Training, formal training, and exercise participation must be pursued
for a minimum of 15 months before determining that training tasks outlined in a QTP and/or TTG cannot
be accomplished.
2. Air Transportation Standardization and Evaluation Program (ATSEP). Air Mobility Command’s
air transportation compliance program executed by commanders at aerial port and air mobility squadron
level. This program provides commanders and AMC/A4T with assessments of a unit’s ability to perform
core air transportation and traffic management procedures ensuring standardized, repeatable, and
technically compliant process execution. AMC active duty, civilian equivalent, reserve and guard
22
personnel activated under Title 10 performing air transportation or traffic management functions while
assigned to an AMC Aerial Port Squadron (APS), Air Mobility Squadron (AMS), Contingency Response
Group (CRG) or to an expeditionary location with similar structure are subject to evaluations under
ATSEP. Logistics Readiness Squadrons with air transportation personnel assigned will follow guidance
outlined in AFI 20-112, Logistics Readiness Quality Assurance Program, and are not subject to AMC
ATSEP requirements. AFRC and ANG MFMs with air transportation personnel will establish guidance to
evaluate/assess their unit’s ability to perform core air transportation procedures.
3. Air Transportation Distant Learning (DL) courses. Completion of applicable courses as defined by
the QTPs and/or TTGs is mandatory to be duty position qualified.
4. Hazardous Material Inspector/Preparer Training Eligibility.
4.1. Hazardous Material Inspector. Hazardous Material Inspector qualification is a requirement and a
necessity for certain functional areas to safely and effectively execute mission responsibilities. Within the
Air Transportation community, Hazardous Material Inspection qualification is required for members
assigned to,and fulfilling duties as Special Handlers and Joint Inspectors.
4.1.1. Initial Eligibility. Members who are currently assigned to a section or aligned to a UTC requiring
Hazardous Material Inspector qualification or have been identified by their respective Functional Area
Manager (FAM) or MFM as requiring Hazardous Material Inspector qualification to fulfill assigned
tasking requirements. Full-Time Equivalents (FTEs), personnel assigned to a Logistics Readiness
Squadron (LRS), and personnel assigned to an Air Transportation Function (ATF) are eligible to pursue
Hazardous Material Inspector qualification regardless of grade or UTC alignment, if the qualification is
required to perform assigned duties.
4.1.2. Refresher Eligibility. Members who are currently qualified as Hazardous Material
Inspectors/Preparers, but no longer meet the initial eligibility criteria listed in Section E, paragraph 4.1.1,
are permitted to maintain a Hazardous Material Inspector qualification and pursue refresher training
through the web-based training found on myLearning. In-residence refresher for members no longer
meeting initial eligibility criteria in Section E, paragraph 4.1.1 is not permitted as a primary option.
4.2. Hazardous Material Preparer. Authorizations for Hazardous Material Preparer qualification is
officially managed under the Traffic Management (2T0XX) career field. Members of the Air
Transportation career field do not have an inherent responsibility to perform hazardous material
preparation and should only do so under unique circumstances. Units should not exceed more than 15% of
their authorized population for Hazardous Material Inspector qualifications with Hazardous Material
Preparers. Only members who meet initial eligibility for Hazardous Material Inspector may pursue
Hazardous Material Preparer qualification/refresher. Members who currently hold a Hazardous Material
Preparer qualification but no longer meet the initial eligibility criteria listed in Section E, paragraph 4.1.1,
may pursue refresher in Hazardous Material Inspector as outlined in Section E, paragraph 4.1.2.
BY ORDER OF THE SECRETARY OF THE AIR FORCE OFFICIAL
LINDA S. HURRY, Maj Gen, USAF
Director of Logistics
DCS/Logistics, Engineering & Force Protection
23
3 Attachments:
1. Qualitative requirements (Proficiency Code Key)
2. 2T2X1 Specialty Training Standard (STS)
3. Contingency/Expeditionary Training Requirements
24
Attachment 1
Qualitative requirements (Proficiency Code Key)
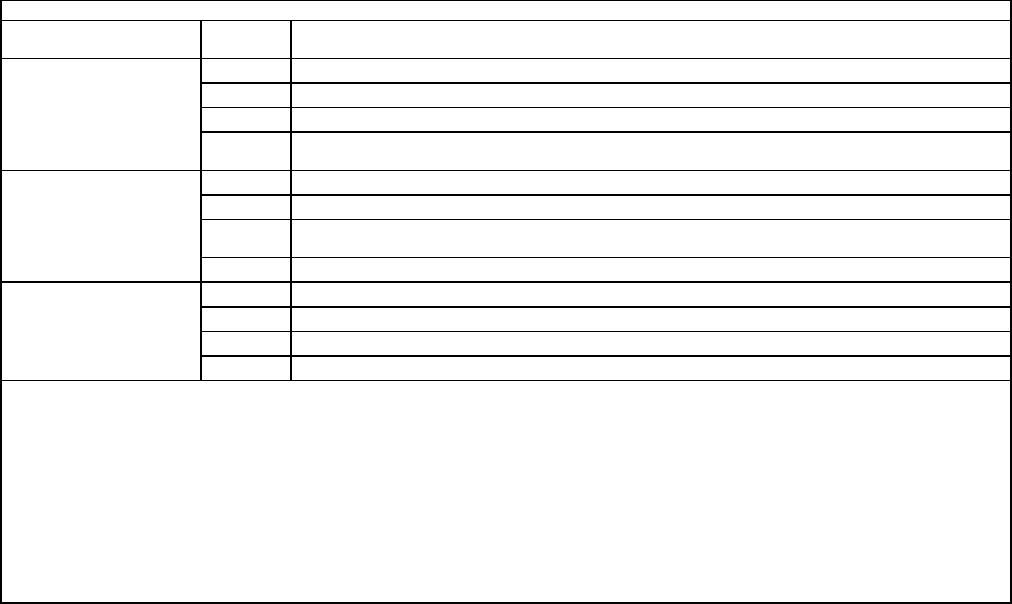
Proficiency Code Key
Scale
Value
Definition: The individual
1
Can do simple parts of the task. Needs to be told or shown how to do most of the task. (Extremely Limited)
Task
2
Can do most parts of the task. Needs only help on hardest parts. (Partially Proficient)
Performance
3
Can do all parts of the task. Needs only a spot check of completed work. (Competent)
Levels
4
Can do the complete task quickly and accurately. Can tell or show others how to do the task. (Highly
Proficient)
a
Can name parts, tools, and simple facts about the task. (Nomenclature)
*Task
b
Can determine step by step procedures for doing the task. (Procedures)
Knowledge
c
Can identify why and when the task must be done and why each step is needed.
(Operating Principles)
Levels
d
Can predict, isolate, and resolve problems about the task. (Advanced Theory)
A
Can identify basic facts and terms about the subject. (Facts)
**Subject
B
Can identify relationship of basic facts and state general principles about the subject. (Principles)
Knowledge
C
Can analyze facts and principles and draw conclusions about the subject. (Analysis)
Levels
D
Can evaluate conditions and make proper decisions about the subject. (Evaluation)
Explanations
* A task knowledge scale value may be used alone or with a task performance scale value to define a level of knowledge for a specific task. (Example:
b and 1b)
** A subject knowledge scale value is used alone to define a level of knowledge for a subject not directly related to any specific task, or for a subject
common to several tasks.
- This mark is used alone instead of a scale value to show that no proficiency training is provided in the course or CDC.
X This mark is used alone in the course columns to show that training is required but not given due to limitations in resources.
NOTE: All tasks and knowledge items shown with a proficiency code are trained during war time.
25
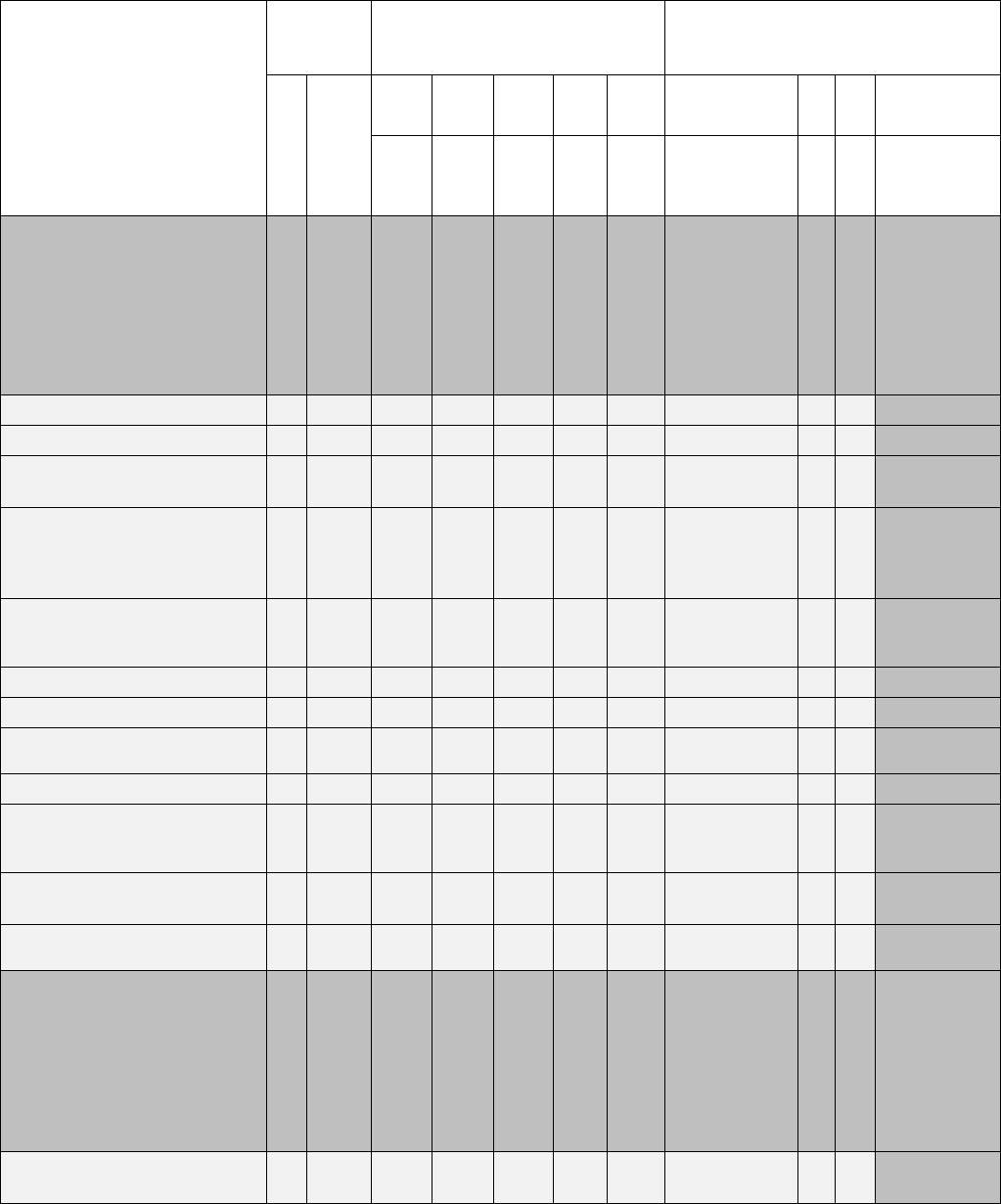
Attachment 2
2T2X1 Specialty Training Standard (STS)
1. Tasks, Knowledge And Technical
Reference(s)
2. Tasks
3. Certification For OJT
4. Proficiency Codes Used To Indicate
Training/Information Provided via ICW
and/or course
Core/Cert^
Deployment*/SEI+
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
Tng
Start
Tng
Complete
Trainee
Initials
Trainer
Initials
Certifier
Initials
3-lvl
5-
lvl
7-
lvl
9-lvl
1 Air Transportation
TR: AFPD: 36-28, AFI 10-
1002, 38-101, 24-605, DTR; J
PUB 3-0, Appropriate aircraft
-1 TO, AFMAN: 11-225, AF
Enlisted Classification
Directory, CFETP 2T2X1
1.1 Career field/progression
5
A
-
-
1.2 Organizational structure
7
A
A
B
1.3 Types and descriptions of
transport aircraft
5
*
A
-
-
1.4 Locate and reference
transportation forms,
publications, and technical
orders
5
*
2b
b
-
1.5 Inspect, inventory, and
store 463L pallets, nets, and tie
down equipment
5
*
b
b
b
1.6 Build-up single pallet
5
*
2b
b
b
1.7 Identify types of shoring
5
*
2b
b
b
1.8 Perform spotter/chocker
duties
5
*
2c
c
c
1.9 Vehicle inspections
5
*
B
-
-
1.10 Perform engine running
offload or on-load (ERO)
operations
*
a
b
-
1.11 Air Transportation
Information Systems
5
*
A
B
-
1.12 Compliance/evaluation
fundamentals
A
A
B
2 Job Related Hazards and
Safety
TR: AFI: 31-7001, 32-2001,
91-20, AFMAN: 32-1067, 32-
7002, 91-201, 91-203,
AFOSH: AFPAM 90-803,
DESR: 6055.09_AFMAN 91-
20
2.1 General hazards and
accident/mishap prevention
5
*
A
B
-
26
2.2 Flight line safety
precautions
5
*
A
B
-
2.3 HAZMAT
Handler/Explosives Safety
5
*
-
-
-
3 Readiness and Mobility
Training
TR: JP 4-0 and 5-0 series,
AFI: 10-403, 10-201, 10-2501,
24-605, 25-101, 32-1020, 32-
1023, 38-101, 90-201, 90-301,
AFPD: 36-1, AFTTP 3-4,
MAJCOM 36-series, DAFI
10-401, DOD 4500.9-R:
Defense Transportation
Regulation (DTR) Part III,
Mobility, AFMAN: 10-2503,
36-2100, 38-102 DAFMAN:
32-1084, Applicable System
User’s Manual
3.1 Deployment Planning and
Execution
7
*
-
B
B
B
3.2 Readiness reporting
9
*
-
-
-
-
3.3 Readiness concepts
9
*
-
-
B
B
3.4 Joint Operation Planning
and Execution System
(JOPES)/ Time-Phased Force
Deployment Data (TPFDD)/
Deliberate and Crisis Action
Planning and Execution
Segments (DCAPES)
9
*
-
-
B
B
3.5 Designed Operational
Capabilities Statement
(DOCS)
9
*
-
-
B
B
3.6 Unit Type Codes (UTCs)
5
*
-
B
B
B
3.7 Installation deployment
training
9
*
-
-
B
B
3.8 Conduct Joint Inspection
(JI) (UFBJT)
*
-
b
-
3.9 Night Vision Goggles
(NVGs)
*
-
-
-
3.10 Emergency Management
(EM)
-
A
B
3.11 Chemical, Biological,
Radiological, Nuclear and
High-Yield Explosive
(CBRNE)
*
-
A
B
4 Operate Vehicles and
Material Handling Equipment
(MHE)
TR: AFI 24-301, 24-302, 24-
605, 91-207, AFMAN 24-306
(I), 91-203, AFTO Form 1800,
Appropriate aircraft -9 T.O.;
Applicable 00, 35 and 36
series T.O./User’s Manual
4.1 Forklifts
4.1.1 Less than 10K forklift
a
-
-
4.1.2 10K Standard
*
a
-
-
27
4.1.3 10K Adverse Terrain
forklift
*
a
-
-
4.2 Tow Vehicle
*
a
-
-
4.3 Aircraft Loaders
4.3.1 25K Aircraft Loaders
-
-
-
4.3.2 Halvorsen Loader
*
a
-
-
4.3.3 Tunner Loader
a
-
-
4.4 Passenger Service
Vehicles
4.4.1 Wide-body Staircase
*
a
-
-
4.4.2 C-5 Staircase
a
-
-
4.4.3 Baggage Conveyor
a
-
-
4.5 Fleet Service Vehicles
4.5.1 Latrine Service
Truck/cart
*
a
-
-
4.5.2 Potable Water Truck
a
-
-
5 Ramp Operations (UFBBR)
TR: DTR, AFPD: 24-6; AFI:
24-605; 11-2C-XXX,
AFMAN: 24-306, 91-203,
DESR: 6055.09_AFMAN91-
201, Appropriate aircraft -1
and -9 T.O.s, Applicable 00
and 36 series T.O.
5.1 General
5.1.1 Select loading equipment
*
a
a
b
5.1.2 Assemble/Set-up aircraft
loads
5
*
2b
b
b
5.1.3 Restrain
cargo/mail/baggage
5
*
2b
b
b
5.2 Loading/Offloading
Aircraft
5.2.1 Prepare aircraft cargo
compartment for loading
*
2b
b
-
5.2.2 Load/offload
cargo/mail/baggage
5
*
2b
b
-
5.2.3 Calculate Tie
down/restrain
cargo/mail/baggage in aircraft
*
2b
b
-
5.3 Perform Load Team Chief
Duties
7
*
-
b
-
6 Air Freight (UFBCP)
TR: DTR, AFPD: 24-6, AFI:
24-603, 24-605, AFMAN: 24-
604, Applicable aircraft -9
T.O., DESR:
6055.09_AFMAN91-201,
Applicable System User’s
Manual
6.1 General
6.1.1 Load/offload trucks
*
-
-
-
6.1.2 Validate proper
packaging, marking, labeling,
and documentation
5
*
2b
b
-
28
6.1.3 Expedited shipment
(AMC MICAP, VVIP, Green
sheet, etc.)
*
A
A
B
6.1.4 Verify size, weight,
destination of shipments
5
*
2b
-
-
6.1.5 Frustrated cargo
5
*
-
-
-
6.2 Cargo Build-Up
6.2.1 Conduct inventory
*
-
-
-
6.2.2 Build multi-pallet train
5
*
2b
b
-
6.2.3 Determine net/gross
weights of
palletized/containerized/rolling
stock shipments
*
2b
b
b
6.2.4 Compute centers-of-
balance for rolling stock,
outsized cargo, and multi-
pallet trains
5
*
2b
b
b
6.3 GATES/Manual Freight
Procedures
6.3.1 Process originating
cargo/mail
*
2b
b
-
6.3.2 Close and Process (CAP)
pallet
*
2b
b
-
6.3.3 Process in transit
cargo/mail
*
2b
b
-
6.3.4 Process terminating
cargo/mail
*
2b
b
-
6.4 Special Handling
6.4.1 Special cargo
A
-
-
6.4.2 Registered mail
*
-
A
B
6.4.3 Classified shipments
*
-
A
B
6.4.4 Frozen, chilled and
perishable shipments
*
-
A
B
6.4.5 Human remains
*
-
A
B
6.4.6 Hazardous Cargo
A
-
-
6.4.7 Inspect hazardous cargo
*
-
a
b
6.4.8 Arms, Ammunition, and
Explosives (AA&E)
*
-
A
B
6.4.9 Nuclear Weapons
Related Material (NWRM)
-
-
-
7 Passenger Services
(UFBML)
TR: DTR, DODI 4515.13,
4500 series,
AFI: 10-403, 24-605,
AFMAN: 34-240, Applicable
System User's Manual
7.1 General
7.1.1 Determine/verify travel
eligibility/priorities
*
2b
b
-
7.1.2 Sign-up passengers
*
2b
-
-
7.1.3 Special Category
passengers
*
A
B
B
29
7.1.4 Brief passengers on
flight information
*
b
b
-
7.2 Passenger terminal
security
A
-
7.2.1 Operate and inspect x-
ray machines, walk-through
magnetometers, and hand-held
magnetometers
-
-
-
7.2.2 Perform
baggage/passenger security
and anti-hijacking inspection
*
b
-
-
7.3 Passenger Processing
7.3.1 Select passengers
*
2b
-
-
7.3.2 Check-in passengers and
baggage
*
2b
-
-
7.3.3 Gate passengers
*
b
-
-
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
5
*
a
-
-
7.4 Baggage Handling
7.4.1 Build-up/breakdown
baggage
5
*
b
-
-
7.4.2 Load/offload baggage
5
*
b
-
-
7.4.3 Process mishandled
baggage
*
a
b
-
7.5 Flight Management
7.5.1 Set up flights
*
2b
-
-
7.5.2 Prepare in-flight meal
requests
-
-
-
7.5.3 Prepare passenger
manifests
*
2b
b
-
7.5.4 Delayed/diverted
passengers
-
A
B
7.5.5 Close out flights
*
2b
-
-
7.6 Manual Procedures
A
B
-
7.7 Funds Management
7.7.1 Passenger Funds
Transaction
-
-
-
7.7.2 Funds Custodian
-
-
-
8 Fleet Service (UFBN2)
TR: AFI: 24-605, Applicable
1C, 13B4 and 36-series
Appropriate aircraft -9 TO,
Applicable System User's
Manual
8.1 General
8.1.1 Prepare fleet service
documents
*
-
-
-
8.1.2 Inventory
expendable/non- expendable
bench stock
-
-
-
8.1.3 Load expendable/non-
expendable items on aircraft
-
-
-
8.1.4 Service/clean air
transportable galley and
lavatories (ATGLs)
*
-
-
-
30
8.2 Clean Fleet
8.2.1 Fill fresh water tanks and
containers
*
-
-
-
8.2.2 Deliver passenger meals
-
-
-
8.2.3 Clean ovens and galleys
-
-
-
8.3 Dirty Fleet
8.3.1 Service aircraft lavatory
systems
*
-
-
-
8.3.2 Remove/dispose of
trash/waste materials from
aircraft
*
-
-
-
9 Load Planning (UFBPL)
TR: DTR, Joint PUB 3-0,
Appropriate aircraft -1 T.O.,
AFI: 10-1002, 24-605,
AFMAN: 11-225, Applicable
System User's Manual
9.1 General
9.1.1 Conduct inventory
*
-
b
b
9.1.2 Identify shipments for
movement
*
-
-
b
9.1.3 Verify shipment
documentation
*
-
-
-
9.1.4 Calculate/validate
shoring requirements
*
-
b
b
9.1.5 Select aircraft loads
*
-
a
-
9.1.6 Prepare
manifests/aircraft package
*
-
a
-
9.1.7 Calculate ACL/Critical
leg ACL
*
-
-
-
9.1.8 Compute aircraft center
of balance
*
-
-
-
9.1.9 Prepare load plan
*
-
-
9.1.10 Hazardous Material
Compatibility
*
-
-
-
9.2 Load Plan Aircraft
9.2.1 C-130
*
-
-
-
9.2.2 C-17
*
-
-
-
9.2.3 C-5
*
-
-
-
9.2.4 KC-10
-
-
-
9.2.5 KC-135
-
-
-
9.2.6 KC-46
-
-
-
9.3 Commercial Aircraft
requirements
*
-
-
-
10 Air Terminal Operations
(UFBAT)
TR: DTR, AFPD: 24- 6, AFI:
24-605, AFMAN: 24-604,
Applicable System User's
Manual
10.1 Information Control
10.1.1 Receive/disseminate
information
*
-
a
b

31
10.1.2 Monitor aircraft ground
operations
7
*
-
a
b
10.1.3 Prepare consolidated
flight package
*
-
a
b
10.1.4 Brief aircrew/troop
commander on load
information
7
*
-
-
-
10.1.5 Accomplish
arrival/departure messages
*
-
a
b
10.1.6 Contract management
-
-
-
10.2 Capability Forecasting
10.2.1 Produce daily/weekly
forecast
7
*
-
a
b
10.2.2 Coordinate mission
requirements
7
*
-
-
-
10.2.3 Complete clearance
requirements
*
-
-
-
11 Data Records
TR: DTR, DODR: 4500
Series, Air Force Master
Catalog, AFPD: 24-6, AFI:
24-605 Series, 33-360, 33-322,
T.O. 00-5-5, Command,
Control, Communications,
Computers and Intelligence
Support Plan (C4ISP) from
GATES
11.1 Review/Maintain
transportation documentation
7
*
-
b
b
11.2 Conduct cargo tracer
action
-
b
b
11.3 Generate Scheduled
Reports
2b
-
-
12 Supervision (UFBXS)
TR: AFI: 23-111, 36-2670, 36-
2406, 36-2907, 36-2502, 38-
101, AFMAN: 36-2100, 38-
102, AFPD: 36-1, AFTTP 3-4
12.1 Property and Resource
Management
7
*
-
-
-
-
12.2 Justify Personnel and
Equipment
7
*
-
-
-
-
12.3 Unit Manpower
Document (UMD)
7
*
-
-
B
B
12.4 Unit Personnel
Manpower Roster (UPMR)
7
-
-
B
B
12.5 Manpower standards
7
-
-
B
B
12.6 Document workload data
7
*
a
b
b
b
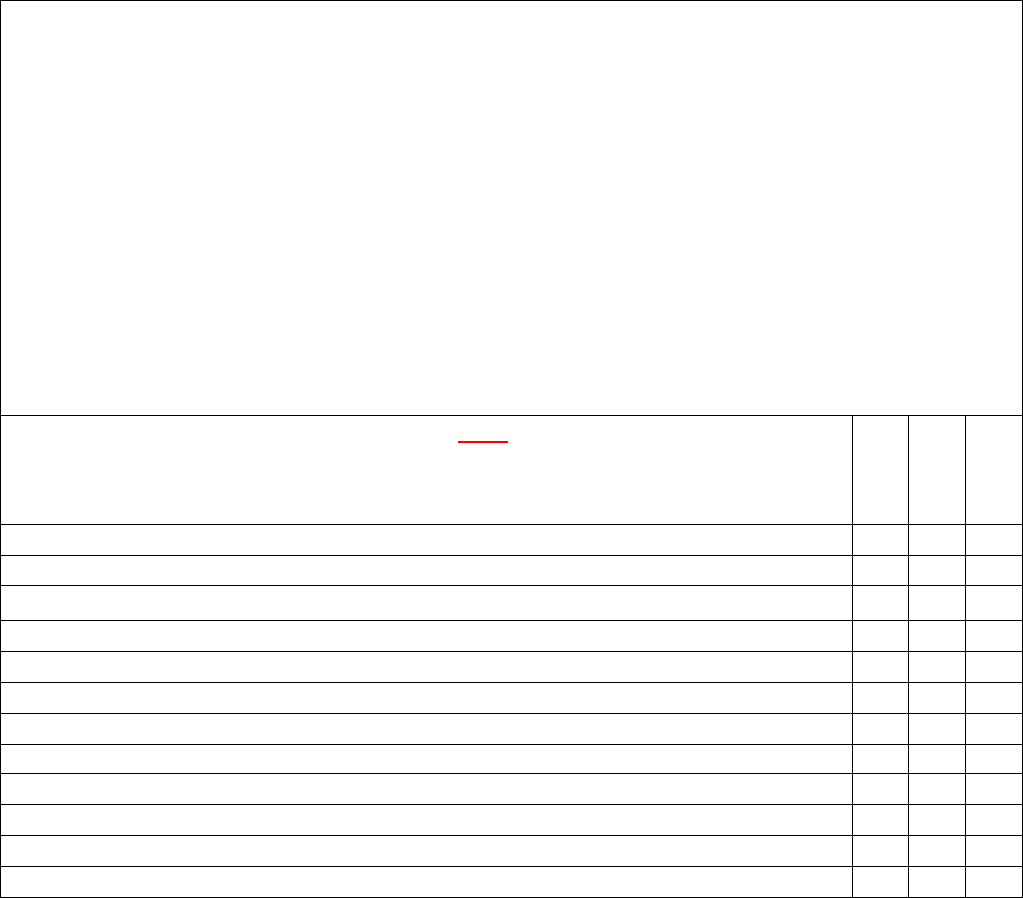
32
Attachment 3
Contingency/Expeditionary Training Requirements
Commanders and supervisors, at all levels, should establish an effective contingency/expeditionary training program taking
into account the normal AEF battle rhythm. The following tables prescribe the minimum training/certification required for
Airmen to meet the stated capability of the Unit Type Code (UTC). As the minimum training requirements, commanders
should use completion of training associated with assigned UTCs as an indicator to determining capability readiness.
Ideally, Airmen should begin the specified training once assigned to their respective UTC. Trainers will assess an Airman’s
ability to perform the required tasks to the “Go”, “No-Go” standard. All appropriate core tasks, in addition to UTC
requirements, must be met.
Mission Ready Airmen: A mission ready 2T2XX will be trained, certified and proficient in the tasks identified in this
CFETP corresponding to their assigned UTC and skill level, to include performing each associated task in MOPP 4.
Mission Ready Airmen are responsible for maintaining individual medical readiness (IMR) and all auxiliary training as
applicable to their assigned UTC.
Crossflow Tasks: Items identified as “Crossflow Tasks” enable qualified Airmen to augment/assist other UTC/functional
area capabilities in a minimal capacity, when not performing duties related to their assigned UTC.
ARC Specific Tasks: Tasks identified in Attachment 3 with an asterisk (*) are additional training requirements for ARC
personnel only and should be included in ARC member training if the necessary resources are available.
The following are critical baseline tasks for ALL Air Transportation
contingency/expeditionary capabilities and required for all 3, 5 and 7-level
members
3-level
5-level
7-level
1.3 Types and descriptions of transport aircraft
X
X
X
1.4 Locate and reference transportation forms, publications, and technical orders
X
X
X
1.5 Inspect, inventory, and store 463L pallets, nets, and tie down equipment
X
X
X
1.6 Build-up single pallet
X
X
X
1.7 Identify Types of shoring
X
X
X
1.8 Perform spotter/chocker duties
X
X
X
1.9 Vehicle inspections
X
X
X
1.10 Perform engine running offload or on-load (ERO) operations
X
X
X
1.11 Air Transportation Information Systems
X
X
X
2.1 General hazards and accident/mishap prevention
X
X
X
2.2 Flight line safety precautions
X
X
X
2.3 HAZMAT Handler/Explosives Safety
X
X
X
33
UTC: UFBAT
AIR TERMINAL OPERATIONS CENTER
(ATOC)
Capable of supporting 1 x aircraft per hour
during 12-hour shift
Description: This UTC provides a two-person air terminal
operations center (ATOC) capability; senior controller,
information control, ramp control, in transit visibility (ITV),
airlift forecasting and records keeping IAW applicable
guidance or directives. ATOC is the operational focal point
and exercises command and control of air transportation work
centers. Coordinates unit move requirements, utilizes
computer-based air transportation systems, briefs cargo and
passenger information to departing aircrews and/or collects
transportation documents on arriving aircraft.
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
10.1.1 Receive/disseminate information
X
X
10.1.2 Monitor aircraft ground operations
X
X
10.1.3 Prepare consolidated flight package
X
X
10.1.4 Brief aircrew/troop commander on load
information
X
X
10.1.5 Accomplish arrival/departure messages
X
X
10.2.1 Produce daily/weekly forecast
X
10.2.2 Coordinate mission requirements
X
10.2.3 Complete clearance requirements
X
11.1 Review/Maintain transportation documentation
X
X
34
UTC: UFBBR
RAMP OPERATIONS
Capable of on or off loading 8 pallet
position equivalents per hour during 12-
hour shift
Description: This UTC provides a four-person ramp operations
capability; Load Team Chief, aircraft on/off Load Team,
Material Handling Equipment (MHE) operators and Engine Run
On/Offload (ERO) IAW applicable guidance or directives. Able
to on/off load organic and/or commercial aircraft with
applicable MHE. Utilize aircraft load plans and computer-based
air transportation systems. When not performing UFBBR
function, can augment following UTCs for these specific tasks:
UFBCP (aircraft pallet build/break) and/or UFBML (passenger
on/off load, baggage on/off load and/or baggage pallet
build/break).
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
4.1.2 10K Standard
X
X
X
4.1.3 10K Adverse Terrain forklift
X
X
X
4.2 Tow Vehicle
X
X
4.3.2 Halvorsen Loader
X
X
X
5.1.1 Select loading equipment
X
X
X
5.1.2 Assemble/Set-up aircraft loads
X
X
X
5.1.3 Restrain cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
X
5.2.1 Prepare aircraft cargo compartment for
loading
X
X
X
5.2.2 Load/offload cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
X
5.2.3 Calculate Tie-down/restrain
cargo/mail/baggage in aircraft
X
X
5.3 Perform Load Team Chief Duties
X
Crossflow Tasks
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
X
X
X
Additional training tasks for ARC only
4.3.3 Tunner Loader
(NOTE: A minimum 50% of personnel assigned
to UTC must be trained)
*
*
*
35
UTC: UFBCP
AIR FREIGHT
Capable of building or breaking 1x
pallet position equivalent every 3
hours during 12-hour shift
Description: This UTC provides a three-person air freight capability;
receive/in-check general/hazardous /special handling cargo, pallet
build-up, break bulk, in transit visibility (ITV) and forklift operator
IAW applicable guidance or directives. Able to review cargo
documentation, build aircraft pallets and/or provide break bulk
support. Utilize computer-based air transportation systems. When not
performing UFBCP function, can augment following UTCs for these
specific tasks: UFBBR (aircraft on/off load) and/or UFBML
(passenger on/off load, baggage on/off load and/or baggage pallet
build/break).
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
4.1.2 10K Standard
X
X
X
4.1.3 10K Adverse Terrain forklift
X
X
X
6.1.1 Load/offload trucks
X
X
X
6.1.2 Validate proper packaging, marking,
labeling, and documentation
X
X
X
6.1.3 Expedited shipment (AMC MICAP,
VVIP, Green sheet, etc.)
X
X
6.1.4 Verify size, weight, destination of
shipments
X
X
X
6.1.5 Frustrated cargo
X
X
X
6.2.1 Conduct inventory
X
X
X
6.2.2 Build multi-pallet train
X
X
X
6.2.3 Determine net/gross weights of
palletized/containerized/rolling stock
shipments
X
X
X
6.2.4 Compute centers-of-balance for
rolling stock, outsized cargo, and multi-
pallet trains
X
X
X
6.3.1 Process originating cargo/mail
X
X
X
6.3.2 Close and Process (CAP) pallet
X
X
X
6.3.3 Process in transit cargo/mail
X
X
X
6.3.4 Process terminating cargo/mail
X
X
X
6.4.2 Registered mail
X
6.4.3 Classified shipments
X
6.4.4 Frozen, chilled and perishable
shipments
X
6.4.5 Human remains
X
6.4.7 Inspect hazardous cargo
X
6.4.8 Arms, Ammunition, and Explosives
(AA&E)
X
Crossflow Tasks
5.2.2 Load/offload cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
X
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
X
X
X
36
UTC: UFBML
PASSENGER SERVICE
Capable of on or offloading 23 passengers and
associated baggage per hour during 12-hour
shift or capable of on or off loading 150
passengers and associated baggage per hour
during 12-hour shift during contingency ops
Description: This UTC provides a four-person passenger
service capability; passenger processing, baggage pallet
build/break, baggage on/off load, in transit visibility (ITV),
staircase truck and material handling equipment (MHE)
operator IAW applicable guidance or directives. Able to
validate travel documentation, manifest, on/off load
passengers, build/break baggage pallets and, with applicable
MHE, on/off load baggage on organic and/or commercial
aircraft. Utilize computer-based air transportation systems.
When not performing UFBML function, can augment
following UTCS for these specific tasks: UFBBR (aircraft
on/off load) and/or air UFBCP (aircraft pallet build/break).
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
4.1.2 10K Standard
X
X
X
4.1.3 10K Adverse Terrain forklift
X
X
X
4.4.1 Wide-body staircase
X
X
X
7.1.1 Determine/verify travel eligibility/priorities
X
X
X
7.1.2 Sign-up passengers
X
X
X
7.1.3 Special Category passengers
X
X
X
7.1.4 Brief passengers on flight information
X
X
X
7.2.2 Perform baggage/passenger security and anti-
hijacking inspection
X
X
X
7.3.1 Select passengers
X
X
X
7.3.2 Check-in passengers and baggage
X
X
X
7.3.3 Gate passengers
X
X
X
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
X
X
X
7.4.1 Build-up/breakdown baggage
X
X
X
7.4.2 Load/offload baggage
X
X
X
7.4.3 Process mishandled baggage
X
X
7.5.1 Set up flights
X
X
7.5.3 Prepare passenger manifests
X
X
7.5.5 Close out flights
X
X
Crossflow Tasks
5.2.2 Load/offload cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
X
37
UTC: UFBN2
FLEET SERVICES
Capable of servicing 2 aircraft latrine and
potable water systems every 3 hours during
12-hour shift
Description: This UTC provides a four-person fleet service
capability; aircraft latrine and potable water service vehicle
operators IAW applicable guidance or directives. Able to
service organic and/or commercial aircraft latrine systems,
potable water systems, remove trash from aircraft IAW local
guidance. Utilize computer-based air transportation systems.
When not performing UFBN2 function, can augment following
UTCS for these specific tasks: UFBBR (ramp operations -
aircraft on/off load) and/or UFBCP (air freight - aircraft pallet
build/break) and/or UFBML (passenger service - baggage
pallet build/break).
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
4.5.1 Latrine service truck/cart
X
X
X
8.1.1 Prepare fleet service documents
X
X
X
8.1.4 Service/clean air transportable galley and
lavatories (ATGLs)
X
X
X
8.2.1 Fill freshwater tanks and containers
X
X
X
8.3.1 Service aircraft lavatory systems
X
X
X
8.3.2 Remove/dispose of trash/waste materials
from aircraft
X
X
X
Crossflow Tasks
5.2.2 Load/offload cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
X
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
X
X
X
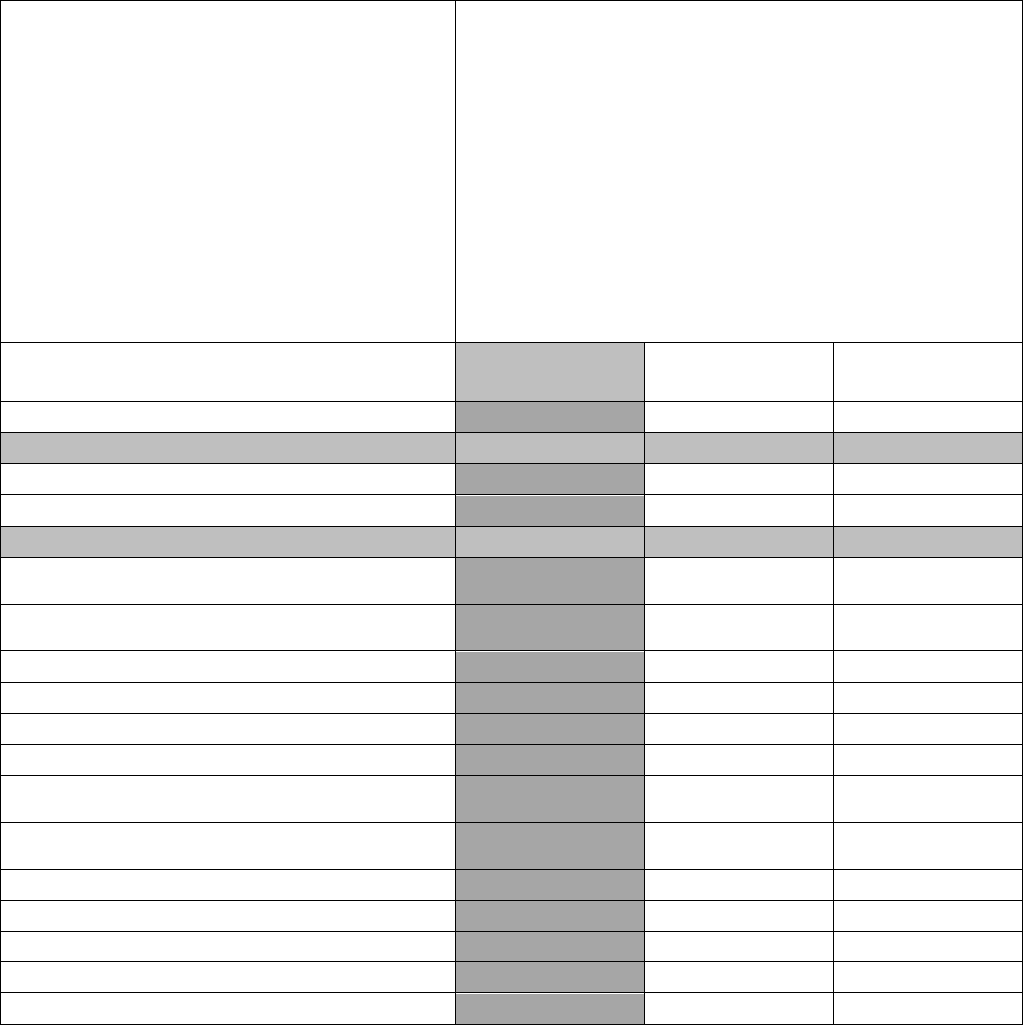
38
UTC: UFBJT
Joint Inspection
Capable of inspecting 21 pallet position
equivalents (PPE) every 3 hours during 12-
hour shift
Description: This UTC provides a two-person joint
inspection (JI) capability; inspect/verify airworthiness,
validate load plan weights/dimensions and verify in transit
visibility (ITV) IAW applicable guidance or directives. Able
to JI unit move cargo and equipment compliance IAW
defense transportation regulation (DTR) and air force manual
(AFMAN) 24-604. Utilize computer-based air transportation
systems. When not performing UFBJT function, can augment
following UTCS for these specific tasks: UFBBR (ramp
operations - aircraft on/off load) and/or UFBCP (air freight -
aircraft pallet build/break) and/or UFBML (passenger service
- baggage pallet build/break).
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
3.8 Conduct Joint Inspection
X
X
Crossflow Tasks
5.2.2 Load/offload cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
X
X
Additional training tasks for ARC only
6.1.2 Validate proper packaging, marking, labeling,
and documentation
*
*
6.1.3 Expedited shipment (AMC MICAP, VVIP,
Green sheet, etc.)
*
*
6.1.4 Verify size, weight, destination of shipments
*
*
6.1.5 Frustrated cargo
*
*
6.2.1 Conduct inventory
*
*
6.2.2 Build multi-pallet train
*
*
6.2.3 Determine net/gross weights of
palletized/containerized/rolling stock shipments
*
*
6.2.4 Compute centers-of-balance for rolling stock,
outsized cargo, and multi- pallet trains
*
*
6.4.2 Registered mail
*
*
6.4.3 Classified shipments
*
*
6.4.4 Frozen, chilled and perishable shipments
*
*
6.4.5 Human remains
*
*
6.4.8 Arms, Ammunition, and Explosives (AA&E)
*
*
39
UTC: UFBPL
LOAD PLANNING
Capable of completing 2 x aircraft load
plans every 4 hours during 12-hour shift
Description: This UTC provides a two-person load planning
capability; select cargo for air movement, verify air worthiness,
calculate aircraft weight/balance and cargo manifesting IAW
applicable guidance or directives. Able to build organic aircraft
load plans IAW applicable aircraft technical orders (to) and air
force manual (AFMAN) 24-604 hazardous material compatibility
chart and coordinate load sequence with commercial aircraft
representatives. Utilize computer-based air transportation
systems. When not performing UFBPL function, can augment
following UTCS for these specific tasks: air terminal operations
center (UFBAT - information control, airlift forecasting, in transit
visibility), and/or UFBBR (ramp operations - aircraft on/off load)
and/or UFBCP (air freight - aircraft pallet build/break) and/or
UFBML (passenger service - baggage pallet build/break).
STS Reference/Training Task
3-
level
5-
level
7-
level
9.1.1 Conduct inventory
X
X
9.1.2 Identify shipments for movement
X
X
9.1.3 Verify shipment documentation
X
X
9.1.4 Calculate/validate shoring requirements
X
X
9.1.5 Select aircraft loads
X
X
9.1.6 Prepare manifests/aircraft package
X
X
9.1.7 Calculate ACL/Critical leg ACL
X
X
9.1.8 Compute aircraft center of balance
X
X
9.1.9 Prepare load plan
X
X
9.1.10 Hazardous Material Compatibility
X
X
9.2.1 C-130
X
X
9.2.2 C-17
X
X
9.2.3 C-5
X
X
9.3 Commercial Aircraft requirements
X
X
Crossflow Tasks
5.2.2 Load/offload cargo/mail/baggage
X
X
7.3.4 Load/offload passengers
X
X
10.1.1 Receive/disseminate information
X
X
10.1.2 Monitor aircraft ground operations
X
X
10.1.3 Prepare consolidated flight package
X
X
10.1.4 Brief aircrew/troop commander on load
information
X
X
10.1.5 Accomplish arrival/departure messages
X
X
11.1 Review/Maintain transportation
documentation
X
X
40
UTC: UFBXS
AIR TRANSPORTATION ADVISOR/TEAM
LEAD
Capable of supporting joint staff, air staff, theater
staff operations, serving as a mobility airlift
advisor or supervising other combinations of air
transportation UTCs.
Description: This UTC provides a one-person air
transportation technical advisor capability; that possess
a wide general knowledge of air transportation systems
and mobility operations to include hub and spoke
dynamics, air transportation organizational constructs
and passenger and cargo movement procedures thru
defense transportation system. UTC will perform and/or
supervise other UTCs performing air transportation
functions IAW applicable guidance or directives. UTC
must be filled by member with awarded 2T271 skill
level. Rank requirement can be waived thru functional
area manager (FAM).
STS Reference/Training Task
7-
Level
3.1 Deployment Planning and Execution
X
3.2 Readiness reporting
X
3.3 Readiness concepts
X
3.4 Joint Operation Planning and Execution System
(JOPES)/ Time-Phased Force Deployment Data
(TPFDD)/Deliberate and Crisis Action Planning and
Execution Segments (DCAPES)
X
3.5 Designed Operational Capabilities Statement (DOCS)
X
3.6 Unit Type Codes (UTCs)
X
12.1 Property and Resource Management
X
12.2 Justify Personnel and Equipment
X
12.3 Unit Manpower Document (UMD)
X
12.6 Document workload data
X
41
UTC: UFBJE
AIR TRANSPORTATION
SUPERVISION (E-8)
Capable of advising Joint Staff, Air Staff or
serve as air transportation operations leader at
all types of locations. UTC should be tasked
when operations have at least 75+ air
transportation personnel.
Description: This UTC provides a one-person air
transportation senior enlisted leader capability;
knowledgeable of sustainment and contingency air
transportation capabilities IAW applicable guidance or
directives. Capable of directing air transportation
operations at all levels and serving as expeditionary
squadron senior enlisted air transportation leader and/or
advisor at either an ELRS, EAMS, or EAPS.
STS Reference/Training Task
9-
Level
3.1 Deployment Planning and Execution
X
3.2 Readiness reporting
X
3.3 Readiness concepts
X
3.4 Joint Operation Planning and Execution System
(JOPES)/ Time-Phased Force Deployment Data
(TPFDD)/Deliberate and Crisis Action Planning and
Execution Segments (DCAPES)
X
3.5 Designed Operational Capabilities Statement
(DOCS)
X
3.6 Unit Type Codes (UTCs)
X
3.7 Installation deployment training
X
12.1 Property and Resource Management
X
12.2 Justify Personnel and Equipment
X
12.3 Unit Manpower Document (UMD)
X
12.6 Document workload data
X
